iSIM
he term “iSIM” stands for Integrated SIM, representing a variant of SIM technology that integrates the functionalities of a traditional SIM card directly into the device’s chipset or processor. Unlike conventional SIM cards, which are physically removable and inserted into a dedicated slot in the device, iSIMs are embedded within the hardware itself. This integration streamlines the device’s design by eliminating the need for a separate SIM card slot, contributing to sleeker and more compact device form factors. Additionally, iSIM technology enhances security by safeguarding sensitive subscriber information within the device’s hardware, offering tamper-resistant protection against unauthorized access or removal.
Here's an overview of iSIM technology:
Embedded Nature: iSIMs do not require a physical SIM card slot because they are completely incorporated into the circuitry of the device. This integration helps create a more streamlined and elegant look while also conserving important internal space.
Functionality: iSIMs carry out every necessary task carried out by conventional SIM cards, even though they are embedded into the hardware of the device. They handle mobile subscriptions, maintain subscriber data, and authenticate the device on the mobile network. These operations are carried out by means of software operating on the chipset of the device, as opposed to depending on an independent physical element.
Flexibility: Since embedded SIMs do not require physical SIM card slots, manufacturers have more freedom to design products thanks to the embedded nature of iSIMs. This adaptability makes it possible to develop devices with smaller, more compact designs and creative form factors.
Remote Provisioning: Just like eSIMs, iSIMs are capable of remote provisioning, which lets consumers activate mobile plans without physically switching SIM cards. The ability to furnish remotely improves consumer comfort and makes it easier to switch between mobile network providers or subscription packages.
Security is the top priority for iSIM technology, which incorporates strong safeguards to protect subscriber data and guarantee secure communication between the device and the mobile network. The purpose of these security measures is to improve user privacy and overall device security by guarding against potential SIM-based attacks and preventing unauthorised access.
differences between eSIM (Embedded Subscriber Identity Module) and iSIM (Integrated SIM), primarily in their implementation and functionality:
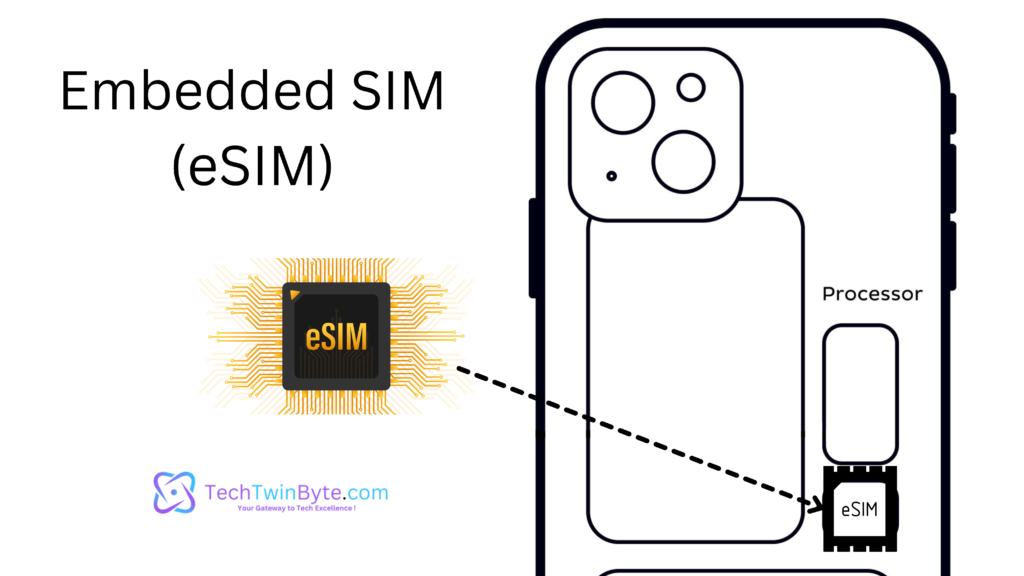
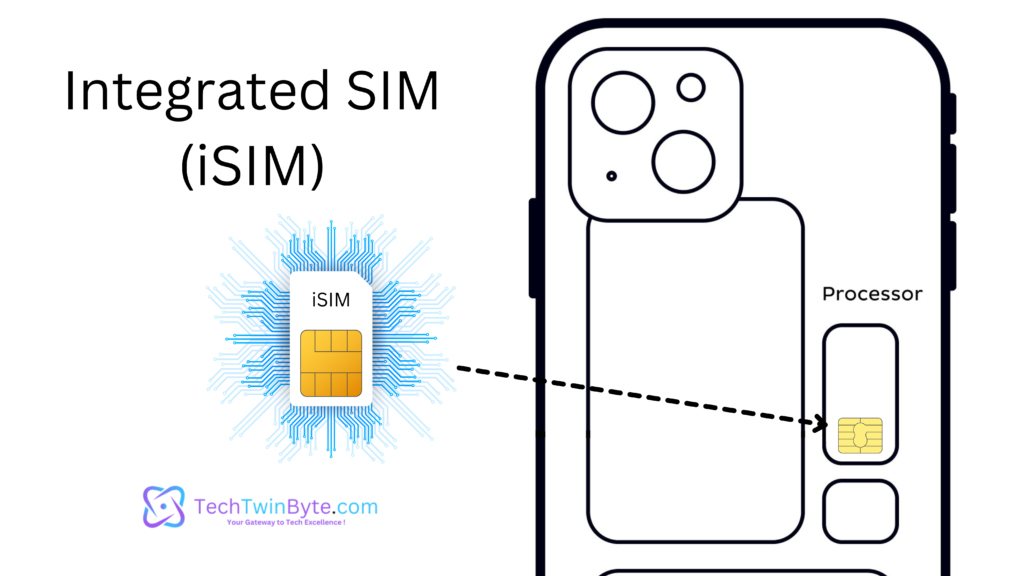
Implementation:
- eSIM physically separate chips embedded within the device’s hardware but are separate from the device’s primary processor or chipset. They are designed to perform SIM functionalities independently and are remotely provisioned.
- iSIM integrated directly into the device’s primary processor or chipset. They function as part of the device’s hardware, eliminating the need for a separate physical SIM chip.
Form Factor:
- eSIM physical chips that are soldered onto the device’s circuit board or embedded within the device’s hardware.
- iSIM physically distinguishable components. They are integrated into the device’s processor or chipset and do not require a separate chip or physical space within the device.
Remote Provisioning:
- eSIM support remote provisioning, allowing users to activate mobile subscriptions over-the-air without physical SIM card swaps.
- iSIM May or may not support remote provisioning, depending on the implementation. Some iSIM implementations may still require physical SIM card activation or provisioning through a different mechanism.
Flexibility and Compatibility:
- eSIM offer flexibility in device design and compatibility, allowing devices to support multiple mobile network operators and switch between them easily.
- iSIM offer flexibility in device design but may have limitations in terms of supporting multiple mobile network operators or switching between them. This depends on the implementation and whether the iSIM is designed for specific networks or purposes.
Security:
- eSIM incorporate security features to protect subscriber information and ensure the integrity of communication between the device and the mobile network.
- iSIM also include security features but may leverage the device’s existing security measures since they are integrated into the device’s primary processor or chipset.
